A VLAN is a logical grouping of network devices put together as a LAN regardless of their physical grouping. VLANs let a user see
and access only specified network segments and limit broadcast domains. This optimizes network efficiency and maintains security access
restriction. VLANs require VLAN capable switches, either implicit (switch only) or explicit (IEEE 802). IEEE VLANs allow multiple VLANs
per adapter or team since both the switch and adapter use a tag in the packet header to sort VLANs.
The Intel PRO/100 VE and VM Desktop Adapters and Network Connections can be used in a switch based VLAN but does not support IEEE Tagging.
The Intel PRO/10 VE, VM adapter has to be placed in an untagged port on that switch, in a single domain.
All other PRO/100+ and PRO/100 S PCI adapters and the PRO/1000 family of server adapters fully support IEEE 802 based VLANs when attached to
an explicit VLAN enabled switch. (NetWare OS require PRO/100 +/S Server adapters).
A VLAN offers you the ability to group users and client PCs together into logical workgroups. This is a critical consideration when connecting clients
to servers that are geographically dispersed across the building, campuses, or enterprise network.
Typically, VLANs consist of a common set of co-workers within the same department but in different locations, a cross-functional team working
on a joint project or, a diverse set of users sharing the same network application. Joining workers across the network forms logical working groups.
VLANs offer the ability to group users and stations together into logical workgroups. This can simplify network administration when connecting clients to servers that are geographically dispersed across the building, campus, or enterprise network.

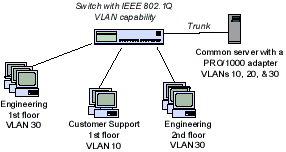
Normally, VLANs are configured at the switch. To set up VLAN membership, your adapter must be connected to a switch with IEEE 802.1Q VLAN capability.
| IMPORTANT: You must use PROSet to add or remove a VLAN in Windows 2000. Do not use the Network and Dial-up Connections dialog box to enable or disable VLANs. Otherwise, the VLAN driver may not be correctly enabled or disabled. Note that you cannot re-enable a VLAN in Windows 2000 once it has been disabled. The server must be restarted to re-enable the connection. |
NetWare versions 4.1x and above support VLANs. To join a VLAN in NetWare applications, you'll need to update your AUTOEXEX.NCF file with LOAD IANS commands.
See the Examples File for detailed instructions on configuring VLANs.
See Installing the eeE DDI8 Driver for UnixWare* 7 for instructions on configuring virtual adapters, teaming, and VLANs in UnixWare 7.1.x.
See instructions in the Linux ANS readme file.