Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
This topic contains supplementary diagnostics and troubleshooting information for PRO/100 S Mobile adapters. This supplementary information is intended for users or network administrators who are already familiar with PRO/100 S Mobile adapters and documentation, and who have run into difficulties after having completed the appropriate installation and troubleshooting procedures for their operating environment.
The following topics are covered in this topic:
-
LED Indicators
-
Windows LAN Diagnostics
-
Troubleshooting Checklist
-
Changing Driver Parameters
-
Modem Installation Troubleshooting
Additional Sources of Information
Consult your computer and network documentation as needed. For the latest technical notes on PRO/100 S Mobile adapters, see the Mobile Release Notes on the Intel Installation CD.
See Intel Support Services for additional information.
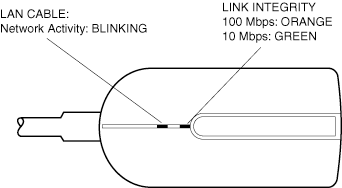
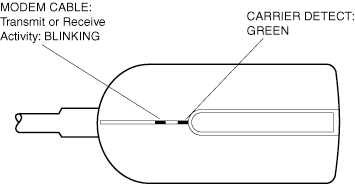
LED Indicators
Type II Adapters, With Cables
The LEDs are located in the cable connector housing, just below the Intel logo. See the diagrams below.
PRO/100 S Mobile Adapter LAN Type II Connector and LEDs
PRO/100 S Mobile adapter modem Type II connector and LEDs
Type III Adapters, Without Cables
The LEDs are located on the left front of the adapter, above the Intel logo. Refer to the bottom of the adapter to identify LED function.
Installing and Using Intel PROSet II
PROSet II is an advanced configuration utility designed by Intel. With PROSet II, you can easily see link and activity status, test hardware, and set standard and advanced adapter features.
To install PROSet II:
-
Insert the Intel CD and wait for the Autorun screen to appear.
-
Click Install Advanced Features on the Autorun screen.
-
When the Component Selection screen appears, choose Intel PROSet II and click Install.
The installer copies the files needed to your computer.
To use PROSet II to run hardware (LAN) diagnostics from Windows:
-
Double-click the Intel PROSet II icon in the Control Panel or the tray icon near the clock on the Windows desktop.
-
Click the Diagnostics tab.
-
Click the Run Tests button. Click Help for details.
-
Click Advanced to run a Sender-Responder test.
-
To check the link and activity status click the General tab.
-
To monitor driver activity driver activity, click the Network Driver tab.
Troubleshooting Checklist
-
Review the Mobile Release Notes on the Installation CD.
-
Be sure you have the current drivers for your adapter. You can check the version numbers on the Intel website at http://support.intel.com.
-
Try reinstalling the adapter drivers. Remove installed drivers first. For Windows 98/95, use Add/Remove Programs in Control Panel. For Windows NT, remove the LAN portion by running Network in Control Panel and the modem portion by running Modems in the Control Panel.
-
When loading drivers or running the test utility, keep the LAN adapter cable attached to the Mobile adapter.
-
Under Novell, ensure that the frame type you are using is the same as that of the file server. The server frame type should be specified as the first frame type in the NET.CFG.
-
In a twisted pair environment, try plugging directly into the hub or concentrator.
-
Plug into a known working network connection.
-
Try using the PRO/100 S Mobile adapter on a different computer.
-
Try another PRO/100 S Mobile adapter, if available.
-
Try forcing the speed and duplex settings on the adapter, as well as the hub or switch to which your adapter is connected.
-
If your computer has multiple PC Card sockets, move the adapter to another socket.
-
If you have more than one PC Card device in your computer, remove the non-Intel PC Card devices.
-
Test the PRO/100 S Mobile adapter without loading Card and Socket Services to prevent conflicts between the Intel adapter and Card and Socket Services.
-
Make sure that the PRO/100 S Mobile adapter interrupt, memory address, and I/O address do not conflict with other installed hardware (such as sound cards, CD-ROM drives and PEN devices).
-
Try loading the Mobile drivers at different memory locations (i.e.: C8000, CC000, D4000, D8000, E2000).
-
Try using different interrupt values (i.e.: 3, 10, 11).
-
Try using different port addresses (i.e.: 280, 290, 310, 320).
-
In Windows 95, change autodetect to specific frame type.
-
In NT (mostly), change the interrupt settings if you experience steady on/off blinking of the link light on a cable connector, or if you experience sporadic mouse movement.
Changing Driver Parameters
For Windows installations, use PROSet II to modify driver parameters such as network speed, duplex, and other advanced settings. In most cases, the default settings for these parameters are best and do not need changing. See Installing and Using Intel PROSet II.
For Novell installations, see the Command Line Keywords and Parameters file on the Intel CD.
Modem Installation Troubleshooting
Review this section if any of the following problems occur:
-
Modem initialization errors occur when attempting to dial out using a communications application
-
Connection fails or other problems occur
It may be necessary to define a modem type within your communications application. If the Intel modem is not listed, choose a "Generic Hayes compatible" device.
If your computer is equipped with an infrared communications port, you may need to disable this port. Such ports often use COM port resources required for other communications devices. Disable the infrared port both in the computer's CMOS or BIOS setup program and the Windows 95 Device Manager as follows:
-
Some computers use a hardware setup utility to configure the infrared port in the BIOS. See your computer documentation.
-
To disable the infrared communications port in Windows 95, go to the Device Manager tab under System in the Control Panel.
-
Double-click the Ports (COM & LPT) entry and the IR Serial Port entry. Check the Disable in this Hardware Profile option to disable the device.
-
You may also need to comment on any "device=" lines containing TRANXIT and in the SYSTEM.INI file. Use a semicolon at the beginning of the line to comment out the line.
Use the Modem Diagnostics Tool to verify the computer-to-modem interface as follows:
-
In the Modems option in Control Panel, click Diagnostics.
-
In Diagnostics properties, highlight the COM port associated with the Intel modem and click the More Info button.
This causes Windows 95 and 98 to send commands to and read responses from the modem, and to display information about the modem and its COM port. The Port Information box should display the following information:
The IRQ and I/O address of the modem's COM port. These should match the physical configuration of the port or modem adapter.
Modem responses to various AT commands. The Intel modem may return ERROR for some AT commands that are not supported. This does not indicate a failure.
-
The Record a Log File option within the Modems option can also help identify modem problems by recording modem commands and responses in a MODEMLOG.TXT file. To create the MODEMLOG.TXT file, go to Control Panel, Modems, Properties, Connection, Advanced. In the Advanced Connection Settings window, place a check mark in the Record a log file option box. A MODEMLOG.TXT file will be created in the C:\WINDOWS directory the next time the modem is used.
For further diagnostics, refer to MDMTST.EXE.